倾向评分匹配
倾向评分匹配/倾向性得分匹配(PSM,Propensity Score Matching)
- 通过观测变量对实验组的预测概率进行匹配
- 处理观察性研究(observational study)的经典方法
- 可以解决内生性问题
适用情形:
- 在观察研究中,对照组与实验组中可直接比较的个体数量很少
- 由于衡量个体特征的参数很多,所以想从对照组中选出一个跟实验组在各项参数上都相同或相近的子集作对比变得非常困难
- 对照组和实验组之间的差异可能是选择性偏差导致的,不一定是干预策略导致的
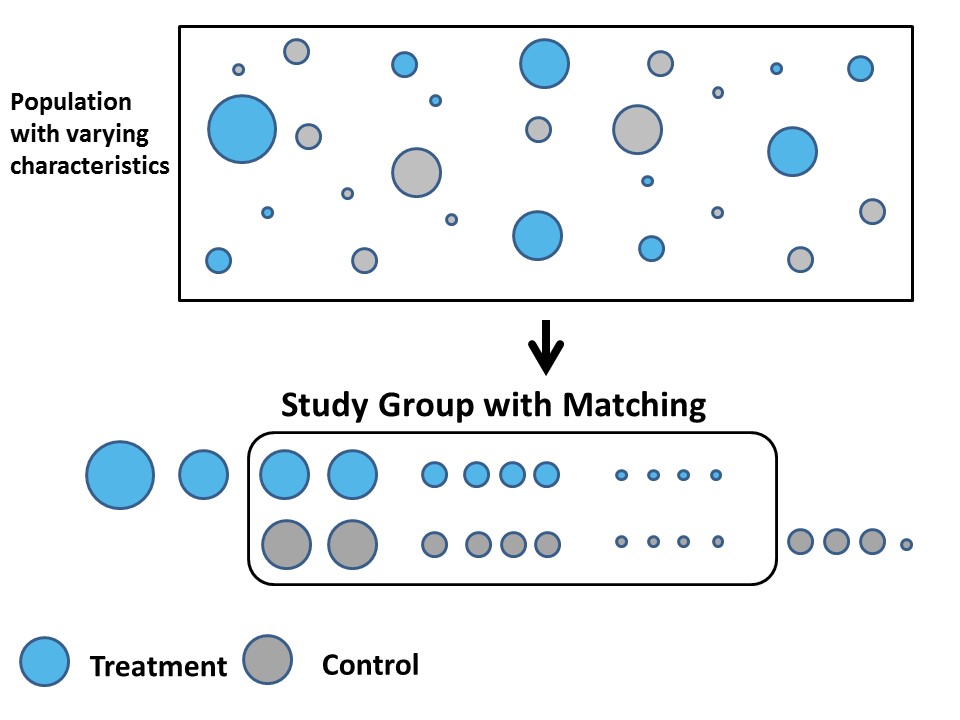
Picture from PROPENSITY SCORE MATCHING(PSM图解)
倾向性得分:一个用户/样本属于实验组的“倾向性”(给定$x$的情况下,样本进入实验组的条件概率)。
$$e(x)=P\left(T=1|X=x\right)$$
其中,
- $T$:干预
- $X$:样本属性/协变量
- $Y$:观测结果/结果变量
Theorem 1: 平衡性质(Balancing Property):
$$T_i \perp X_i \mid e(X_i)$$
Theorem 2: 无混淆(Unconfoundedness):
$$ T_i \perp Y_{i0}, Y_{i1} \mid e(X_i)$$
- 倾向性得分是一种“Balancing score”
- 对于倾向性得分$e(X_i)$相同的一群用户$i$:
- 干预$T_i$和特征$X_i$是独立的
- 干预$T_i$和潜在结果$Y_{i0}, Y_{i1} $是独立的
- 当协变量$X$不影响干预变量$T$、但影响结果变量$Y$时,引入协变量可以提高干预精度
- 当遗漏了重要的协变量时,会导致偏差
前提/假设
PSM需满足以下两个前提/假设:
- 条件独立假设:控制了协变量后,样本是否接收干预与潜在结果相互独立
- 共同支撑条件:若匹配结果较为理想,匹配后的两条核密度曲线较为相近
匹配方法
PSM通过统计模型对每个样本计算倾向性得分,再按照倾向得分是否接近进行匹配。
以分组变量为解释变量(分类变量),样本属性(可能会影响到结果的变量)作为被解释变量,进行逻辑回归(Logistic Regression),从而计算每个样本的倾向性得分。
- 一对一匹配:在控制组中选择与实验组样本最相近的单个样本进行匹配
- 优点:匹配的样本之间较为相近,偏差较小
- 缺点:样本匹配量小、估计的方差较大
- 一对多匹配:在控制组中选择多个与实验组样本相近的样本进行匹配
- 缺点:在控制组中找到的第2个、第3个、……样本与实验组样本的近似性会减弱,会增大估计的偏差
控制组样本量较多时,可以考虑使用一对多匹配
| 匹配方法 | 特点 | 偏差 | 方差 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 最近邻匹配 | 增加近邻数,可重复使用 | ||
| 半径匹配 | 容忍度增加 | ||
| 核匹配 | 带宽增加 | ||
| 卡尺匹配 | 容忍度增加 | ||
| 分块匹配法 |
最近邻匹配
最近邻匹配(Nearest-neighbor Matching):选择控制组中倾向性得分最接近的样本作为匹配样本
干预样本$i$与无干预样本$j$相匹配:
$$
\begin{equation}
\mid p_i - p_j \mid = \min_{k \in { T=0 } } \left\lbrace \mid p_i - p_k \mid \right\rbrace
\end{equation}
$$
半径匹配
半径匹配(Radius Matching):
核匹配
核匹配(Kernel Matching)
卡尺匹配
卡尺匹配(Caliper Matching):给定误差 $\delta > 0$,干预样本$i$与无干预样本$j$相匹配
$$
\begin{equation}
\delta > \mid p_i - p_j \mid = \min_{k\in { T=0 } } \left\lbrace \mid p_i - p_k \mid \right\rbrace
\end{equation}
$$
- 可能会有样本找不到匹配对象
分块匹配法
分块匹配法(Stratification)
匹配效果检验
应用因果推断方法尽可能保证干预组与控制组的分布较为相近(尽可能在已观测到的变量上同质),尽可能去“模拟”随机试验的情况,需要结合一定检验方法来检验“模拟”效果,以保障因果推断评估结果的稳健性(Robust)。
共同支撑检验
共同支撑检验(Common Support Test):为了提高匹配质量,仅保留倾向得分重叠部分的个体(会损失一定的样本量)。
方法:
- 比较匹配前后的核密度图
- 绘制条形图,显示倾向得分的共同取值范围
平衡性检验
平衡性检验(Balance Diagnose):观察匹配后的各个变量的均值是否有显著差异。计算每个变量的干预组和虚拟控制组的差异(SMD,Standardized Mean Difference)。
$$
\begin{equation}
\mathrm{ SMD } = \frac{ \bar{ X }{ \mathrm{ Treat } } - \bar{ X }{ \mathrm{ Control } } }{ \sqrt{ \frac{1}{2} \left( s^2_{ \mathrm{ Treat } } + s^2_{ \mathrm{ Control } } \right) } }
\end{equation}
$$
- 相关论文:Zhang, Z., Kim, H. J., Lonjon, G., & Zhu, Y. (2019). Balance diagnostics after propensity score matching. Annals of translational medicine, 7(1).
- 经验表明,如果一个变量的SMD不超过0.1,一般认为这个变量的匹配质量可以接受;否则,需要结合经验来判断该变量是否可以剔除。
反驳式检验
反驳式检验(Refute):
- 添加随机混杂因子:添加随机的混杂因子(控制特征),如果因果效应变化较小,表明PSM结果较为稳健
- 安慰剂检验:将干预替换为随机变量,如果因果效应接近于0,表明PSM结果较为稳健
反驳式检验本质上是弱检验,检验通过表明PSM估计结果在已有的控制变量上能够保持较好的稳健性;检验不通过,则认为PSM估计结果是不可用的,需要重新评估。
敏感性分析
敏感性分析(Sensitivity Analysis):TBD
Pros & Cons
优势 Strengths
- 在计算倾向性得分时,考虑了交互项(interaction terms)
- 可用于二分变量(dichotomous variables)和连续变量(continuous variables)
- 较少依赖于p值或其他特定于模型的假设
局限性 Limitations
- 需要大样本(PSA works best in large samples to obtain a good balance of covariates.)
- 要求控制组和实验组有较大的共同取值范围(Group overlap must be substantial to enable appropriate matching.)
- 要尽可能控制可观测的变量,如果存在不可观测的协变量,会导致“隐形偏差”(The most serious limitation is that PSA only controls for measured covariates. Matching on observed covariates may open backdoor paths in unobserved covariates and exacerbate hidden bias.)
- 没有考虑样本的聚集性,邻域层级的研究可能会存在问题(Does not take into account clustering (problematic for neighborhood-level research).)
Python
pymatch
- GitHub地址:https://github.com/benmiroglio/pymatch
- 不要使用
pip install pymatch安装,应下载修正版至pymatch同名文件夹,直接加载使用
- 不要使用
compare_continuous会报错,相应解决方案可参考https://github.com/benmiroglio/pymatch/issues/36- 可使用
causalinference包计算ATE(参考Causal Inference fro the Brave and True - Propensity Score - Propensity Score matching)
causalinference
- 官方地址:https://causalinferenceinpython.org/
- GitHub地址:https://github.com/laurencium/Causalinference
- 计算ATE:https://matheusfacure.github.io/python-causality-handbook/11-Propensity-Score.html#propensity-score-matching
DoWhy
相关资料:
- [ZhiHu]因果推断框架 DoWhy入门
实例
伪Demo(pymatch)
1 | # 载入需要的库 |
- 计算显著性差异所需的最小样本量:Post not found: 数据分析-ABtest「样本量」小节
R
Matching
- 使用
Matching包实现PSM
1 | ## 安装Matching包 / install Matching package |
匹配
1 | Y <- lalonde$re78 |
匹配效果
1 | MatchBalance(Tr ~ age + I(age^2) + educ + I(educ^2) + black + hisp + |
参考资料/推荐阅读
- [Blog] 因果推断漫谈(二):倾向性得分匹配介绍
- [ZhiHu] PSM的原理及STATA操作
- [ZhiHu] 聊一聊因果推断中的ATT、ITE、ATE和CATE
- [JianShu] PSM倾向得分匹配法学习指南
- Propensity Score Analysis
- An Introduction to Propensity Score Matching
- Caliendo M, Kopeinig S. Some practical guidance for the implementation of propensity score matching [J]. Journal of economic surveys, 2008, 22(1): 31-72.
- Austin, Peter C . An Introduction to Propensity Score Methods for Reducing the Effects of Confounding in Observational Studies [J]. Multivariate Behav Res, 2011, 46(3):399-424.
- 倾向得分匹配(PSM)的原理以及应用
- Why is Average Treatment Effect different from Average Treatment effect on the Treated?
- PROPENSITY SCORE MATCHING(PSM图解)
软件实现
- STATA: Implementing Propensity Score Matching Estimators with STATA
- R: Multivariate and Propensity Score Matching Software for Causal Inference
- R: Sekhon J S . Multivariate and Propensity Score Matching Software with Automated Balance Optimization: The Matching package for R [J]. Journal of statistical software, 2011, 42(i07).


